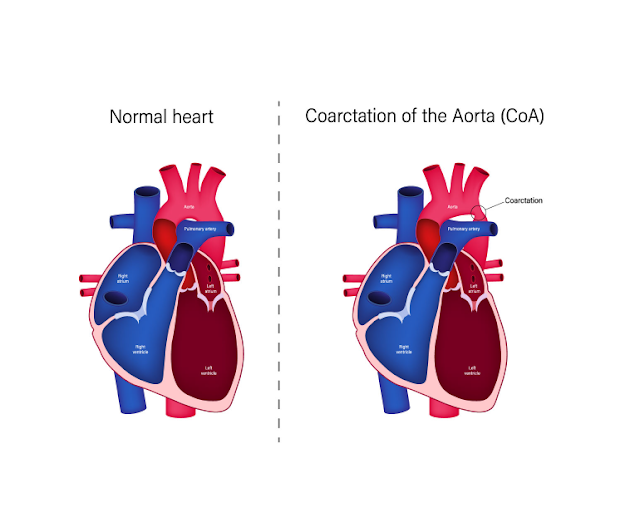
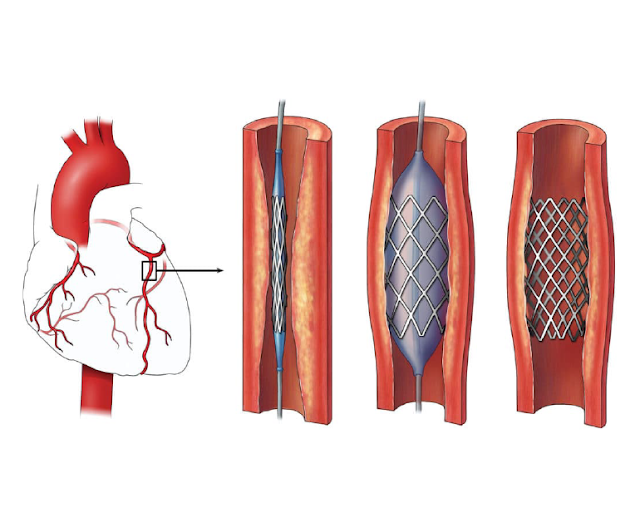
What is Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging?

Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR), also known as cardiac MRI, is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging technique that provides detailed information about the structure and function of the heart. It utilizes a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create high-resolution images of the heart, allowing healthcare professionals to evaluate cardiac anatomy, assess myocardial function, and detect various cardiovascular conditions. CMR works by aligning the hydrogen atoms in the body's tissues using a strong magnetic field. When radio waves are applied, the hydrogen atoms emit signals that are captured by specialized detectors, enabling the creation of detailed images. By manipulating different imaging parameters, such as magnetic field strength and timing, CMR can provide a wealth of information about the heart's structure and function. One of the main applications of CMR is the assessment of myocardial function. It can accurately measure the heart's pumping capacity...